Precision Hardware Customized Solutions Manufacturer
Laser marking is a precise, permanent method for labeling components in manufacturing. A laser marking machine emits a focused beam of light (via an oscillator, scanning mirror, and lens) to etch or color the surface of a material. Because it uses light energy, laser marking produces marks that resist wear and fading. In practice, three types of laser marking dominate industry use: Fiber, CO₂, and Ultraviolet (UV) lasers.
Each type offers distinct capabilities depending on the material (metal, plastic, glass, etc.) and the application. In this guide, we explain the characteristics of each type of laser marking, compare their advantages, and help you choose the best solution for your needs.
Contents
“Types of laser marking” refers to the different laser sources available for marking. The three main categories are:
Fiber Laser Marking: Uses an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements to generate an infrared laser (typically ~1064 nm).
CO₂ Laser Marking: Uses a gas mixture (CO₂, nitrogen, helium) in a sealed tube to produce a far-infrared laser (10.6 μm).
UV Laser Marking: Uses frequency-converted lasers to generate ultraviolet light (around 355 nm).
Each of these laser technologies creates marks by ablating or annealing the surface, but their beam characteristics differ significantly. Below, we detail each type of laser marking:
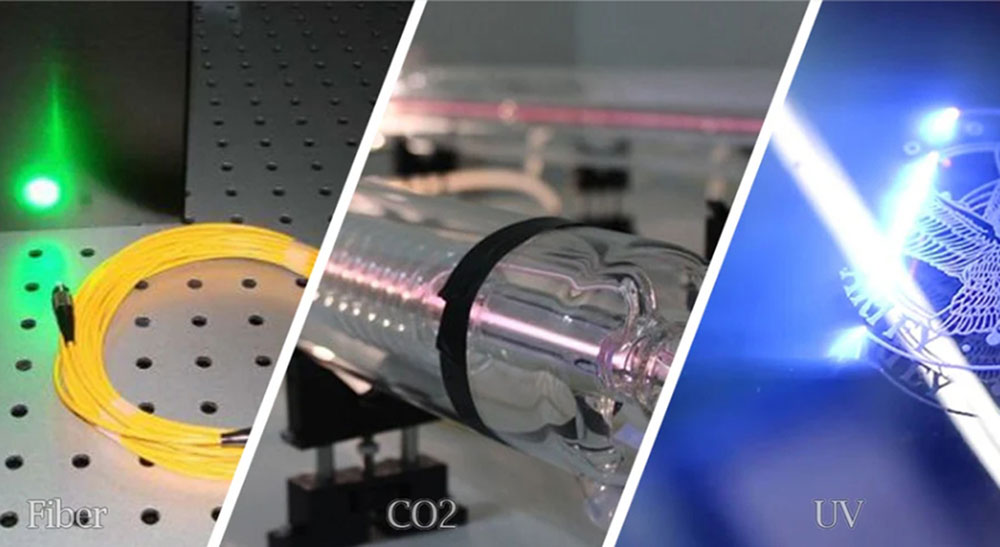
Fiber lasers emit infrared wavelengths (typically 780–2200 nm) that are ideal for metal marking. A fiber laser marker focuses a tiny, powerful beam onto the material, allowing it to engrave or anneal surfaces with high precision. These systems are fast and highly accurate, producing deep, permanent marks even on hard metals like stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and alloys.
Fiber markers can also mark certain plastics, stone, leather, and rubber. Many industries—such as aerospace, automotive, electronics and jewelry—rely on fiber laser marking for serial numbers, part identifiers, logos and barcodes.
Advantages: Fiber lasers require minimal maintenance and have long lifetimes. They produce deep, high-contrast marks on metals without the need for consumables. The beam spot is very small, so even tiny text or complex graphics come out clean and legible.
Applications: Commonly used on metal components (fasteners, engine parts, electronic enclosures, tools) and some hard plastics. Because of their speed and power, fiber lasers excel in high-throughput metal engraving.
Considerations: Fiber laser systems tend to be more expensive initially. They are less effective on non-metallic or transparent materials (e.g. glass, wood), since infrared light is not absorbed well by those substrates.
“Fiber laser markers have minimal maintenance requirements and long-lasting durability… They are highly effective at engraving and marking metals, making them versatile tools”.
CO₂ lasers operate at a much longer wavelength (~10.6 μm) compared to fiber lasers. They use a gas tube containing CO₂ (along with other gases) that emits light when electrically excited. This beam interacts strongly with organic and non-metal materials. In fact, CO₂ lasers are especially effective on wood, paper, leather, fabrics, glass, and plastics.
The heat from the beam vaporizes or carbonizes the surface, creating high-contrast marks or engravings. Industries like packaging, signage, textiles and plastics fabrication widely use CO₂ marking for logos, codes, and decorative patterns.
Advantages: CO₂ lasers are cost-effective and can produce fast engraving speeds on non-metallic materials. They create sharp marks on acrylics, glass, wood, textiles, ceramics and rubber. For example, CO₂ markers easily engrave acrylic sheets, cut leather, and mark cardboard with high quality.
Applications: Ideal for plastics and organic parts – think product labels, instrument panels, or wooden signs. Common uses include pharmaceuticals and food packaging (marking expiration dates or lot codes), textiles (branding clothes), and crafts (engraving wood or leather).
Considerations: The 10.6 μm laser energy is poorly absorbed by metals; metal parts generally reflect most of the beam. Thus, CO₂ systems are not suitable for metal engraving. Also, the large beam size means CO₂ lasers have lower marking resolution compared to fiber or UV lasers.
“CO₂ laser markers work effectively on organic materials. They cost less than fiber lasers and can provide fast engraving speeds… best on non-metallic materials”.
UV lasers emit ultraviolet light (around 355 nm), which is much shorter in wavelength than infrared. This tiny beam enables “cold marking”: the high-energy UV photons break molecular bonds directly rather than heating the material bulk. As a result, UV marking produces extremely fine, shallow etches with almost no heat-affected zone.
UV lasers can mark almost any material, including plastics, glass, sapphire, ceramics, silicon, and even transparent films. They are often used for ultra-fine graphics, micro-drilling, and high-contrast logos where precision is critical.
Advantages: UV lasers offer exceptional versatility and precision across a wide range of materials. Since the process adds very little heat, delicate or heat-sensitive substrates (like medical plastics or semiconductor wafers) won’t deform. The marks are crisp and high-resolution. UV systems also tend to have a long service life and low maintenance thanks to solid-state components.
Applications: Common in electronics, medical, aerospace and packaging. For instance, UV lasers are used to mark micro-features on circuit boards, drill tiny holes in glass, label pharmaceutical vials, and cut precise patterns on silicon wafers.
Considerations: UV laser machines are more expensive due to complex optics and cooling. They are typically used only for marking/engraving – not heavy cutting – so their application scope is narrower. However, their ability to produce fine detail often outweighs the cost for high-value parts.
“The UV laser’s wavelength is one-third the size of a standard laser’s wavelength, creating superior detail… This marking process is called ‘cold marking.’ The UV light breaks bonds preventing overheating”.
When choosing a laser marking solution, consider how each type matches your needs:
Material Compatibility: Fiber lasers excel on metals. CO₂ lasers excel on organic/non-metal materials like plastics, wood and glass. UV lasers work on virtually all materials (including plastics, glass, thin metals and semiconductors).
Wavelength & Precision: A shorter wavelength allows finer detail. UV lasers (~355 nm) have about 3× shorter wavelength than fiber lasers (~1064 nm), so UV marking yields extremely fine, microscopic features. Fiber lasers provide very precise marking on metals. CO₂ lasers (10.6 μm) create deeper, high-contrast marks but with coarser resolution.
Marking Speed: Fiber lasers typically deliver the fastest marking on metal due to high power density. CO₂ lasers can mark plastics and wood very quickly as well. UV lasers may require slower scanning speeds to achieve their ultra-fine marks, but still offer high-throughput for precision work.
Cost & Maintenance: CO₂ laser systems are generally least expensive to buy and maintain. Fiber lasers cost more upfront but have lower operating costs and minimal maintenance. UV lasers are usually the most costly, but their high precision can justify the investment for specialized applications.
In practice, the choice often comes down to the primary material and mark requirements. For example, metal fabricators overwhelmingly choose fiber lasers for serializing metal parts, while a packaging plant might favor a CO₂ laser for coding cardboard and plastics. If you need the highest resolution on a delicate substrate, a UV system may be the best option.

Industrial buyers value laser marking for its clear business benefits. Across fiber, CO₂ and UV technologies, common advantages include:
Permanent, Durable Marks: Laser-etched codes cannot be rubbed off or washed away. Unlike ink or labels, the marking is integral to the material, ensuring long-term readability.
High Speed & Efficiency: Marking with lasers is almost instantaneous. This is far faster than traditional etching or printing methods, which can involve multiple steps and downtime for consumables. Rapid marking keeps production moving.
Broad Material Compatibility: Laser markers handle a vast range of substrates. From metals and plastics to glass, wood, rubber and ceramic, there’s a suitable laser type for nearly every material. This versatility means one technology can often replace several older marking processes.
No Consumables: Lasers use light only – there are no inks, solvents or stamps to replace. This reduces maintenance, waste and downtime. Consequently, laser marking is cleaner and more eco-friendly.
High Precision & Quality: All laser types produce high-contrast, machine-readable marks. Even very small text and fine graphics (like 2D barcodes or logos) are crisp and consistent. This precision improves traceability and aesthetics.
Resilience to Harsh Conditions: The permanent marks created by lasers withstand extreme environments. For example, laser markings on medical devices survive repeated sterilization, and marks on automotive parts endure heat, corrosion and blasting.
“Laser marking machines mark permanently. The marks cannot be rubbed off or fade away through time or exposure to contaminants”.
In summary, laser marking (in its various forms) offers industrial buyers durable identification, faster throughput, and lower long-term cost compared to inkjet printing, stamping or chemical etching. These benefits translate to higher productivity and better quality control for manufacturers of electronics, automotive, medical devices, packaging, and more.
When you need reliable, high-quality laser marking on metal or plastic parts, Shengwo Machinery is the partner you want. As a specialized sheet metal fabrication and machining company, Shengwo combines advanced laser technology with manufacturing expertise. Our fiber, CO₂ and UV laser systems are integrated into a full production line, ensuring precision from raw metal to finished part.
Expertise and Quality: We use industrial-grade laser markers and have trained engineers who optimize every job. Shengwo’s website highlights that our laser marking yields “highly accurate, clear, and long-lasting results”. We strictly control each step, from setting parameters to final inspection, so your logo or code is perfectly clear. In fact, Shengwo advertises “high-precision laser marking, clear and permanently traceable” output.
Fast Turnaround: With streamlined processes and efficient scheduling, we deliver projects quickly. Clients can expect rapid quotes and fast production. As Shengwo notes, our “streamlined processes and efficient production schedules” lead to rapid turnaround times. We recognize that in business, time is money – so we keep your order on schedule.
Comprehensive Service: Beyond marking, Shengwo handles laser cutting, bending, welding and finishing in-house. This one-stop capability means better coordination and consistency. Whether it’s a prototype batch or large volumes, our capacity (over 10 years of experience and dozens of machines) lets us flexibly meet your needs.
Customer Support: You’ll have Shengwo’s engineers by your side from start to finish. We offer guidance on material selection, design tweaks, and marking options. This expert support helps you choose the right type of laser marking for your application, saving time and ensuring success.
In short, choosing Shengwo Mechanical means choosing reliability, precision and peace of mind. We invest in the best equipment and the right talent so you get top-notch laser marking that boosts your product quality.
Fiber, CO₂ and UV lasers each offer unique strengths for industrial marking. Fiber lasers deliver speed and durability on metal; CO₂ lasers offer cost-effective marking on plastics, glass and wood; UV lasers provide unmatched precision on all substrates. Understanding these types of laser marking lets manufacturers match the right technology to their materials and production goals. For companies needing durable, high-resolution marks (from serial numbers to branding), lasers are usually the superior choice.
At Shengwo, we help you navigate these options. Our comprehensive capabilities in sheet metal fabrication and marking ensure that no matter which laser type you need, the result is clear, permanent, and exactly to spec. We invite you to contact Shengwo Mechanical today. Let our experts assess your requirements and provide a custom solution that elevates your product’s quality and traceability. Don’t settle for fading ink or unreliable labels – get in touch now to start your laser marking project with confidence!
Q: What are the different types of laser marking?
A: The three main types of laser marking are fiber, CO₂, and UV lasers. Each uses a different laser source: fiber lasers (infrared), CO₂ lasers (far-infrared gas), and UV lasers (ultraviolet light). These types cover most industrial marking needs.
Q: How do fiber, CO₂, and UV laser marking differ?
A: They differ mainly in wavelength and application. Fiber lasers (around 1064 nm) are best for engraving metals, providing high speed and precision. CO₂ lasers (10.6 μm) work excellently on non-metals like plastics, glass, and wood. UV lasers (355 nm) offer ultra-fine marking on almost any material, with very little heat effect. Each requires specific equipment, so the choice depends on your material and detail requirements.
Q: Which type of laser marking is best for metal parts?
A: Fiber laser marking is generally the best choice for metals. Its infrared beam is well absorbed by metal surfaces, producing clear, durable marks. Fiber lasers can quickly engrave stainless steel, aluminum, titanium and more with high contrast. CO₂ and UV can mark metal too, but they may require special coatings or settings; fiber is usually preferred for straight metal applications.
Q: Can laser marking be used on plastics and other non-metals?
A: Yes. CO₂ lasers are ideal for many plastics (ABS, PVC, etc.), as well as rubber, wood and glass. UV lasers can mark plastics like PE, PP, and PET with extremely fine detail. Even transparent plastics and delicate materials respond well to UV marking. Fiber lasers can mark some plastics too, but they shine primarily on opaque, darker materials.
Q: Are laser marks permanent and durable?
A: Absolutely. Laser marking creates permanent indents or color changes in the material. These marks do not rub off or fade under normal conditions. In fact, laser-etched text and codes resist harsh conditions – medical parts retain their markings after sterilization, and metal components keep their laser marks through heat, chemicals and abrasion. This permanence is a key reason industries rely on laser marking for traceability.
Q: Why should I choose Shengwo Mechanical for my laser marking needs?
A: Shengwo is an experienced precision manufacturer that offers state-of-the-art laser marking combined with comprehensive metal fabrication. We use high-end equipment to achieve “highly accurate, clear, and long-lasting results”.
Our team delivers projects on time, and we provide expert support from design to delivery. As Shengwo notes, we guarantee “consistent quality, competitive pricing, and reliable delivery timelines.” When you partner with Shengwo, you get top quality markings and full service support.