Прецизионная аппаратура Производитель индивидуальных решений
Contents
Expert sheet metal fabrication for automotive, aerospace, and more. High-precision solutions tailored to your industry needs for superior performance.
Sheet metal fabrication is an essential process in modern manufacturing, transforming flat sheets of metal into complex components and structures for a wide range of industries. This versatile technique is pivotal for creating parts with high precision, making it the backbone of industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the techniques, applications, and advantages of sheet metal fabrication, while highlighting the expertise of a precision sheet metal fabricator.
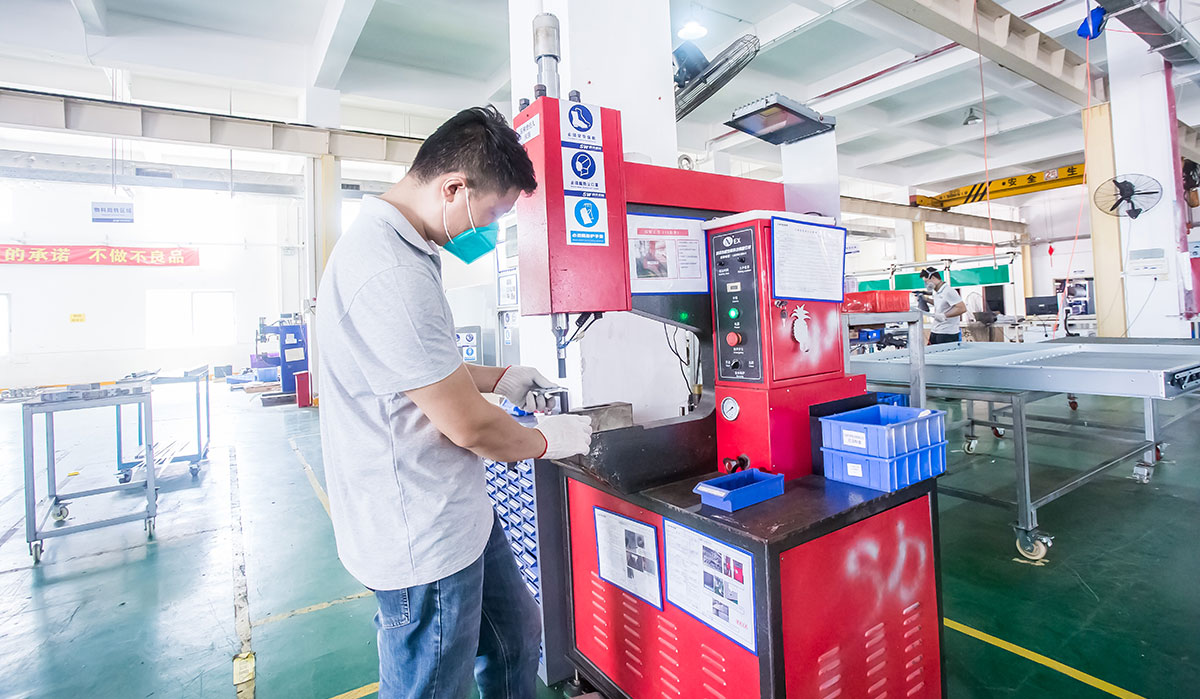

Sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling thin metal sheets to create components or end products. These sheets typically range from 0.5mm to 6mm in thickness and can be made from materials such as aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, and copper. Each material choice depends on the application, as different metals offer varying characteristics such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weight.
A precision metal fabricator employs advanced machinery and techniques to achieve tight tolerances and superior quality. Their role is vital in industries that require complex parts where accuracy, consistency, and reliability are paramount.
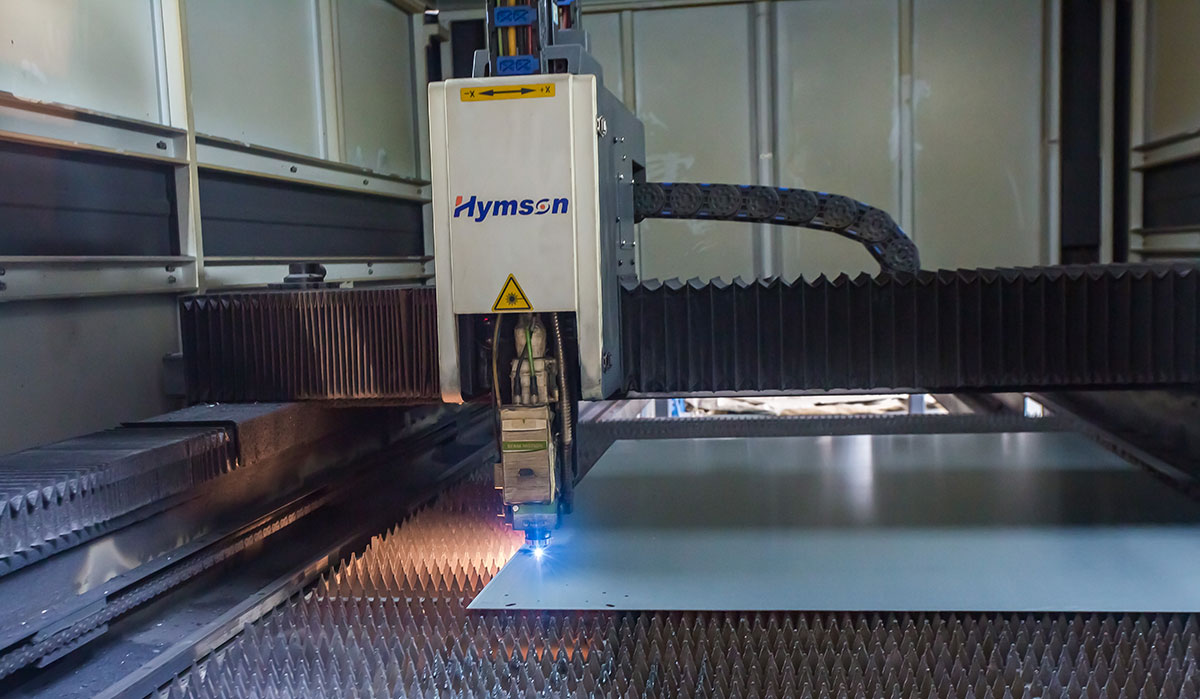

Sheet metal components are extensively used for vehicle body panels, chassis, brackets, and other structural parts. Precision fabrication ensures durability and performance, contributing to vehicle safety and aerodynamics.
In aerospace, where weight reduction and strength are critical, metal fabrication is indispensable. Components such as fuselage parts, wings, and engine components are manufactured with extreme precision to meet stringent safety and performance standards.
Fabrication techniques are critical for creating enclosures, brackets, and casings for electronic devices. Proper shielding and ventilation designs ensure functionality and longevity.
Customized metal components are widely used in architectural projects for aesthetic and functional elements, including roofing, façades, staircases, and support structures.
Precision metal fabrication plays a crucial role in manufacturing diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and patient care devices, where hygiene and accuracy are critical.
The flexibility of sheet metal fabrication allows for creating parts with complex geometries tailored to specific requirements. This adaptability is crucial in industries requiring bespoke solutions.
Advanced techniques ensure components meet stringent specifications, achieving tight tolerances crucial for high-performance applications.
Fabricated metal components offer superior strength and resistance to environmental factors, making them ideal for use in harsh conditions.
Automation and efficient fabrication processes reduce production costs. This affordability benefits both low-volume and high-volume production runs.
Modern fabrication techniques enable quick prototyping, reducing lead times for product development and market launch.
Automation has transformed the sheet metal industry. Robotic arms and automated systems perform repetitive tasks with precision, enhancing productivity and reducing labor costs.
CNC technology revolutionizes the fabrication process by allowing precise and repeatable cuts, bends, and punches.
The integration of 3D printing with traditional sheet metal fabrication opens new possibilities for complex designs and rapid prototyping.
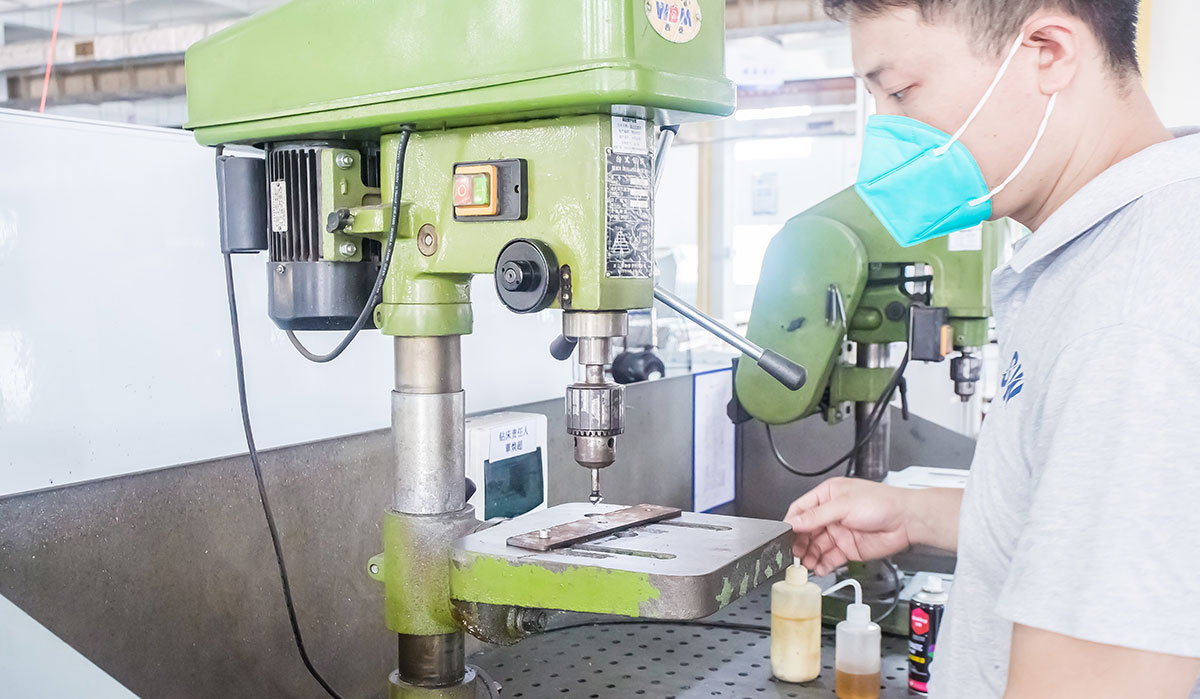

Partnering with a skilled precision sheet metal fabricator provides access to cutting-edge technology, experienced professionals, and innovative solutions tailored to meet specific needs.
Sheet metal fabrication remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, providing high-quality components for countless industries. By leveraging the expertise of precision sheet metal fabricators, businesses can achieve superior results, maintain competitive advantages, and meet evolving market demands. Understanding the techniques, applications, and technological advancements outlined in this guide empowers manufacturers to fully harness the benefits of sheet metal fabrication.